plprot
- BY-2 cell culture plastids ["proplastids"]
|
Further details in:
Baginsky et al., Journal of Proteome Research 3, 1128-1137
|
BY-2 cell culture plastids resemble proplastids. They are undifferentiated with few
internal structures, contain nucleoids similar to proplastids (Philips et al., 2002)
and they exhibit a DNA synthesis pattern that is similar to proliferating plant cells
(reviewed in Sakai, 2004). Furthermore, they have a proplastid like transcription
system that is dominated by NEP-type transcription, i.e. NEP-promoter consensus elements
direct transcription initiation in BY-2 plastids (Sakai et al., 1998, Kapoor and
Sugiura, 1999). And last, they have retained a limited ability to develop and
differentiate, i.e. auxin depletion induces amyloplast formation (Miyazawa et al., 1999).
We could futhermore show, that BY2 plastids do not accumulate protochlorophyllide, even
after aminolaevulinic acid feeding to stimulate tetrapyrrole biosynthesis (Siddique,
Gruissem and Baginsky, unpublished).
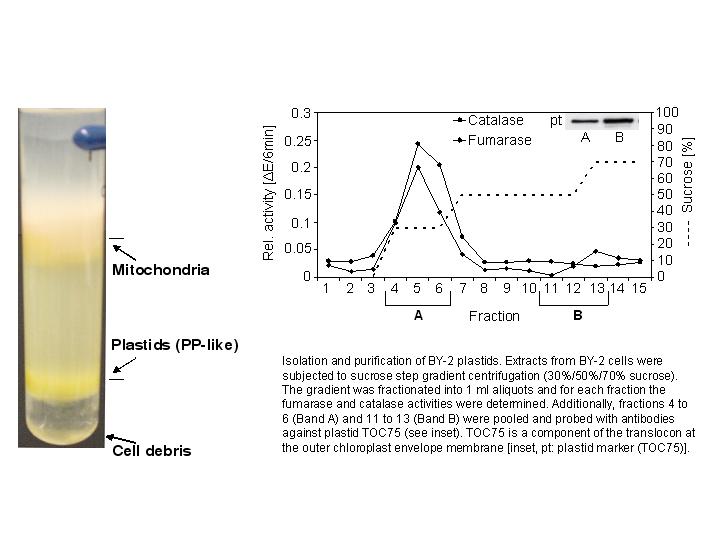
For our analysis, we have isolated BY-cell culture plastids by Sucrose density gradient
centrifugation using a combination of a step- gradient and linear gradient. The purity
was checked by antibody assays using marker proteins from other cell organelles together
with enzymatic measurements (FIGURE 1). With the isolated plastids, we devised a
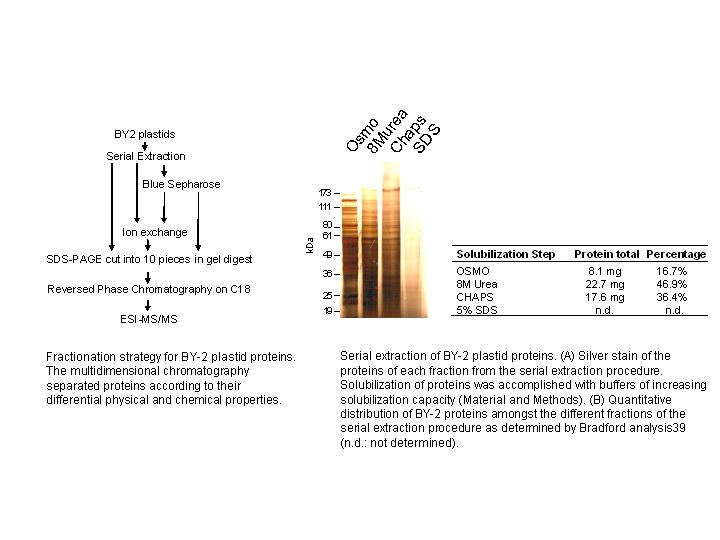
multidimensional protein fractionation strategy that was based on the different
solubility of the proteins (Serial extraction), their charge and their ability to bind
to purine nucleotides (FIGURE 2). Each chromatographic fraction was subjected to SDS
PAGE, in gel tryptic digest and LC-ESI mass spectrometry on an ion trap as described
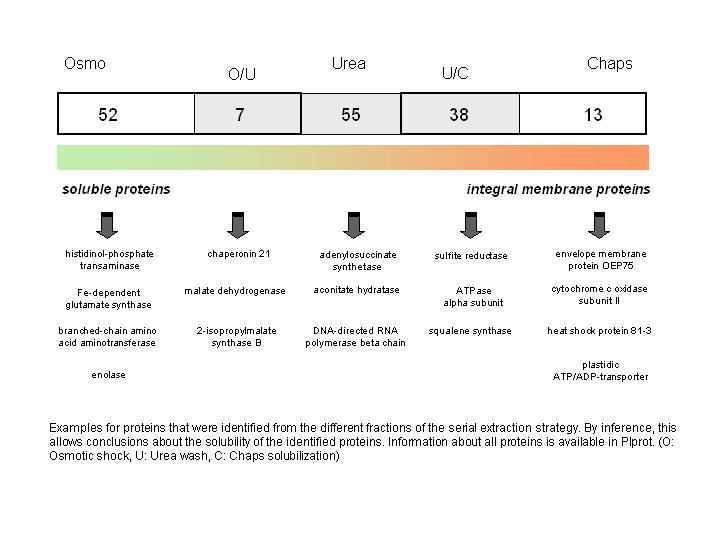
(Baginsky et al., 2004). Information about protein solubility and in vivo membrane
attachment can be concluded from the partition of the identified proteins in the
different fractions of the serial extraction procedure. Examples for all different
solubility categories (a protein that was found in the osmotic shock fraction (O)
was considered soluble, a protein that was detected only after washing the membranes
with 8M urea was considered peripherallly attached to the membrane and proteins that
were detected only after solubilization of the membranes with detergent were considered
strongly attached or integral membrane proteins) are provided in FIGURE 3. Information
about all identified proteins is deposited in plprot, that can be searched by either
key word or by BLAST search.
References: Philips et al., 2002, Planta 215, 258-66; Sakai et al., 1998,
Plant Cell Physiology 39, 928-934; Kapoor and Sugiura, 1999, Plant Cell 11,
1799-1810; Sakai et al., 2004, International Reviews in Cytology 238, 59-118;
Baginsky et al., 2004, Journal of Proteome Research 3, 1128-37.
|
Top
|
Top
|
Top
|
|